All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesExtraction of non-living resources includes extraction of minerals (rock, metal ores, gravel, sand, shell), oil and gas (including infrastructure, salt and water.
Overall, these activities generated 22.88 billion EUR in Gross Value Added (GVA) and employed an estimated 0.17 million people in 2017.
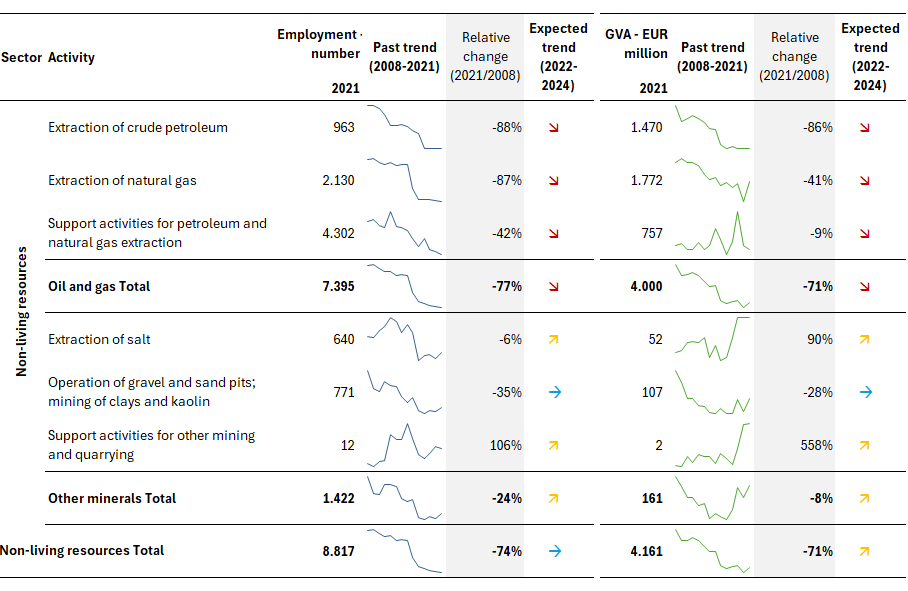
In the EU-27, the extraction of non-living resources sector (excluding water) generated EUR 4.2 billion and over 8.8 thousand jobs in 2021 (Table 1).
Table 1:
Read more on these activities
Extraction of Minerals
Extraction of Oil and Gas, including infrastructure
Extraction of Salt
Pressures on the marine environment
The extraction of non-living resources puts numerous pressures on the marine environment including:
- Physical loss and disturbance of the seabed is a pressure imposed by the extraction of non-living resources, for example underwater plumes caused by the extraction of minerals and aggregates result in both the direct removal and smothering of marine habitat and species.
- Hydrographical changes can be caused by large scale operations, for example by relocation of sediments or constructions at sea;
- Contamination is dependent on the technologies used but is caused by; for example, from resuspension of polluted sediments, emissions from ships, oil and gas related discharges and other equipment used in the processes;
- Introduction of underwater noise and other forms of energy is related to all activities above. Continuous noise is caused by operation of ships and equipment for dredging. Oil and gas operations cause emissions of impulsive underwater noise during construction phase, while continuous noise emissions are related to regular operation of equipment.
- Eutrophication can be aggravated in the eutrophic areas by the extraction of resources which cause resuspension of nutrients from sediments.
References
- ↵European Commission, Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries, Joint Research Centre, Borriello, A., Calvo Santos, A., Codina López, L. et al., The EU blue economy report 2024, Publications Office of the European Union, 2024, https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2771/186064